Analysing GW150914
For a brief overview of the analysis and results on a simulated signal, see Overview.
Below we analyse the first observed gravitational-wave signal, GW150914 (Phys
.Rev.Lett. 116 (2016) 6,061102,
Phys.Rev.Lett. 116 (2016) 24,241102), using the
simple_pe_pipe executable. The following config file can be used:
1[pesummary]
2trigger_time=GW150914
3channels={H1:GWOSC, L1:GWOSC}
4outdir=outdir
5accounting_group=UNKNOWN
6accounting_group_user=albert.einstein
7f_low=20
8f_high=2048
9#trigger_parameters={mass_1: 36.8, mass_2: 32.0, spin_1z: -0.62, spin_2z: 0.47, chi_p: 0.1, time: 1126259462.41}
10trigger_parameters=trigger_parameters.json
11approximant=IMRPhenomXPHM
12asd={H1:GW150914_H1_asd.txt,L1:GW150914_L1_asd.txt}
13generate_corner=True
and this can be launched with:
simple_pe_pipe config.ini
Here, we specify the time of the event based upon the event identifier in the
GWOSC database. The trigger_parameters file
contains the approximate parameters of the event, which are used to seed the
optimization routine. The asd dictionary contains pointers to the
instrumental sensitivity curves.
Note
The auxiliary data can be downloaded from here.
Below is a corner plot showing the obtained posterior distribution when
using the IMRPhenomXPHM waveform model (Phys.Rev.D 103 (2021) 10,
104056):
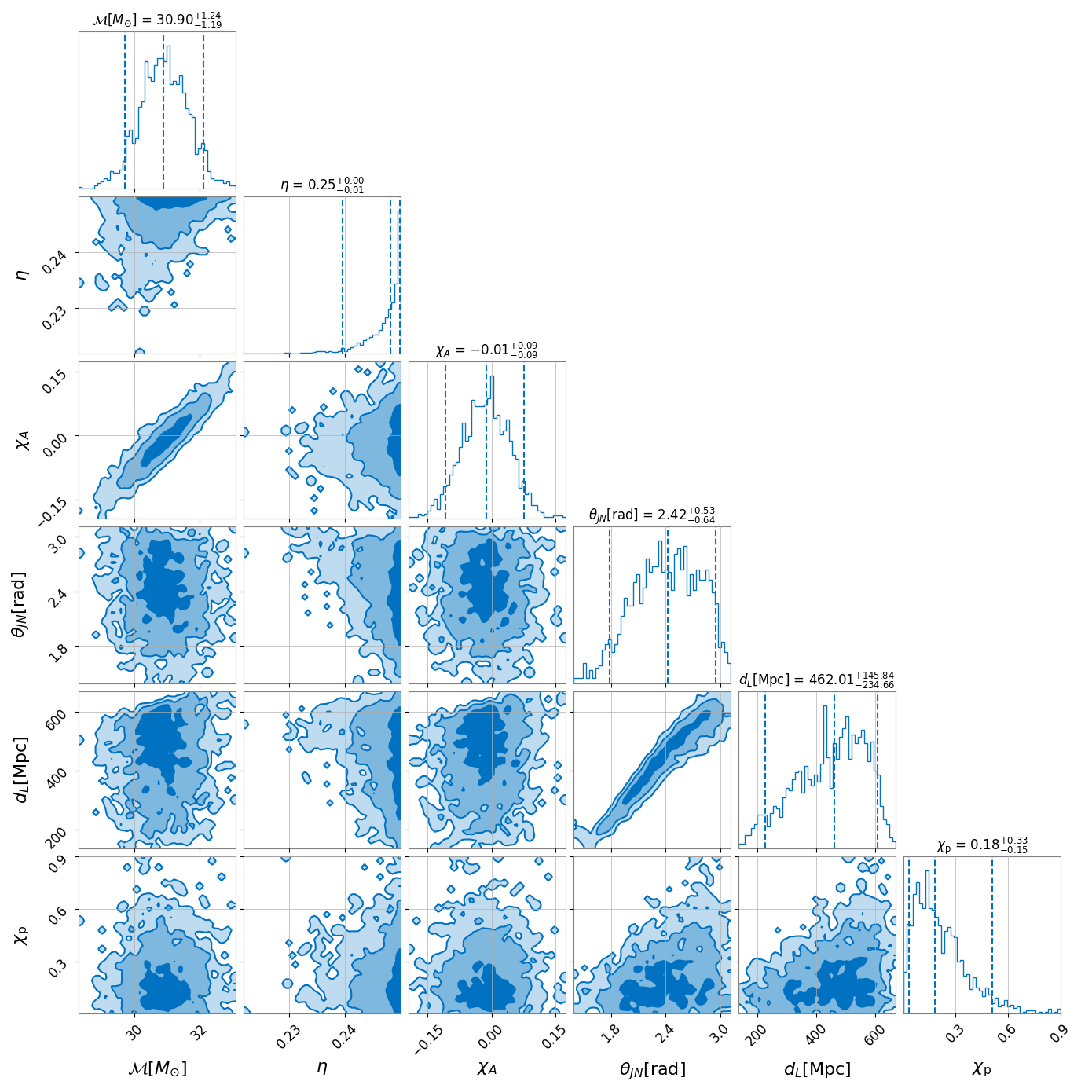
and below is a corner plot showing the obtained posterior distribution when
using the IMRPhenomTPHM waveform model (Phys.Rev.D 105 (2022) 8,
084040):
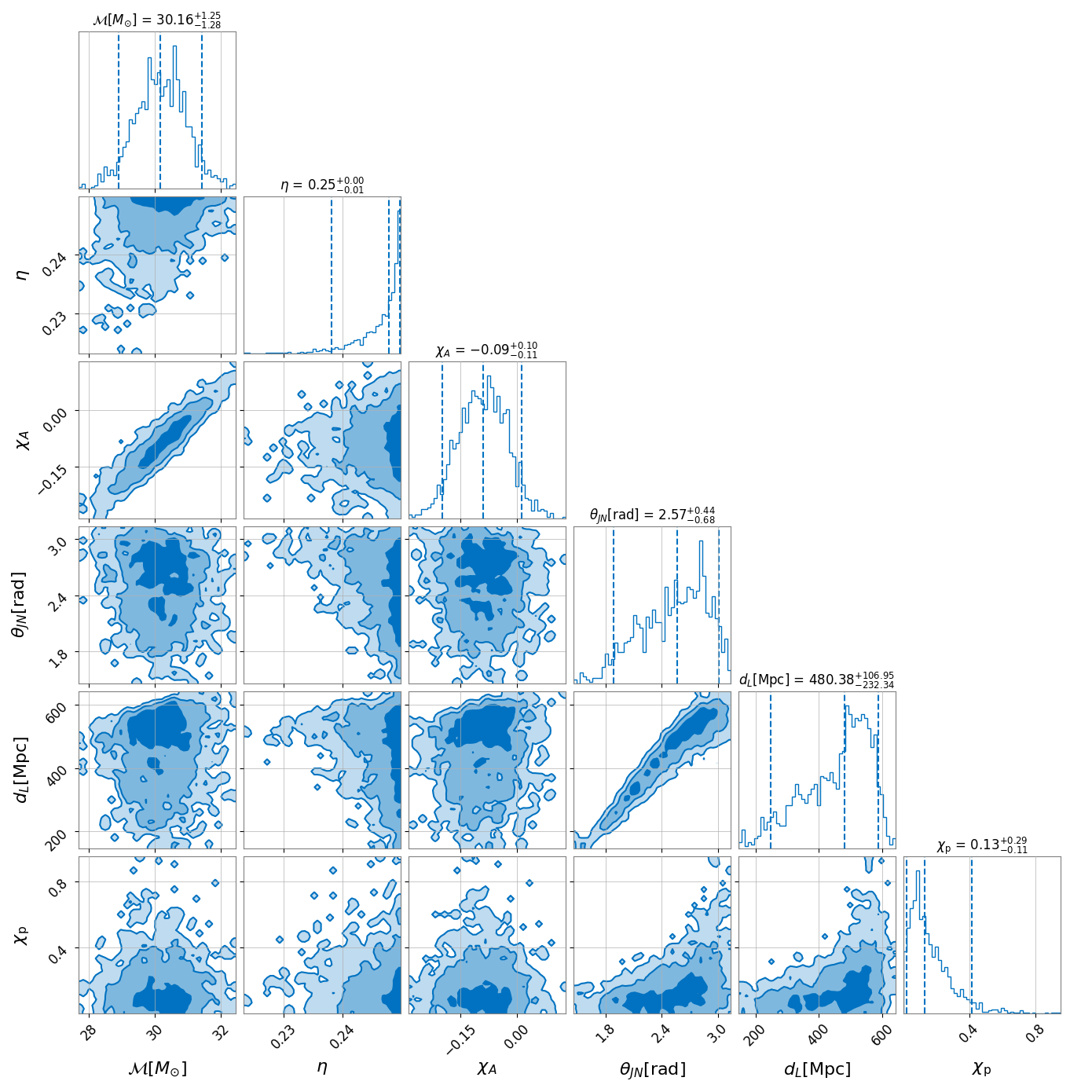
Both of these analyses were performed as part of simple-pe’s
continuous integration and are therefore using the latest version of the code.
Note
This research has made use of data or software obtained from the Gravitational Wave Open Science Center (gwosc.org), a service of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration, the Virgo Collaboration, and KAGRA. This material is based upon work supported by NSF’s LIGO Laboratory which is a major facility fully funded by the National Science Foundation, as well as the Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC) of the United Kingdom, the Max-Planck-Society (MPS), and the State of Niedersachsen/Germany for support of the construction of Advanced LIGO and construction and operation of the GEO600 detector. Additional support for Advanced LIGO was provided by the Australian Research Council. Virgo is funded, through the European Gravitational Observatory (EGO), by the French Centre National de Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), the Italian Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (INFN) and the Dutch Nikhef, with contributions by institutions from Belgium, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Japan, Monaco, Poland, Portugal, Spain. KAGRA is supported by Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) in Japan; National Research Foundation (NRF) and Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) in Korea; Academia Sinica (AS) and National Science and Technology Council (NSTC) in Taiwan.